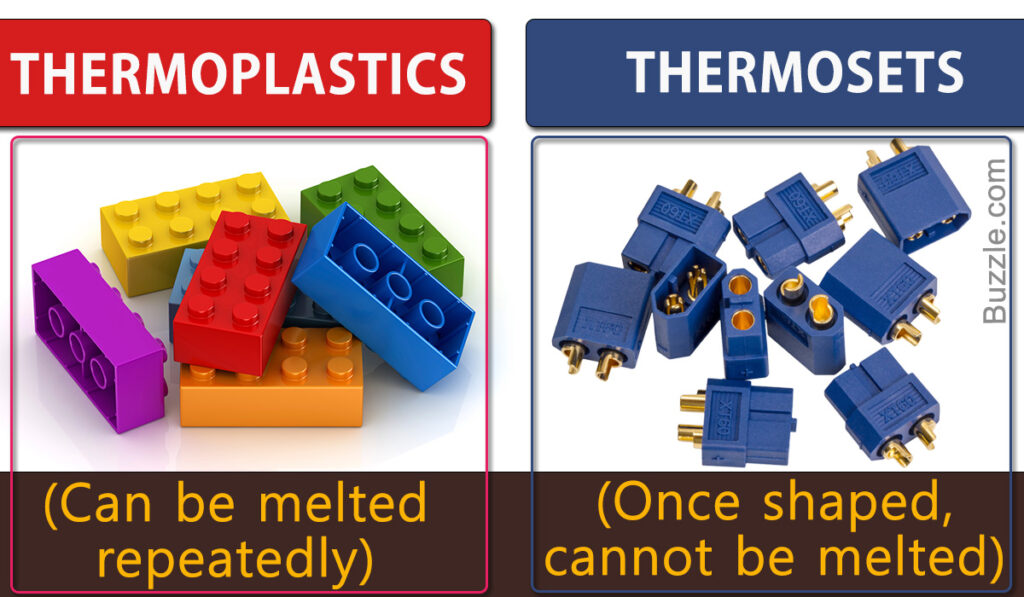
Did you know that there are two kinds of plastic? Thermoplastic and thermoset. We get the name plastic from thermoplastic material. So what’s the difference?
Polymers
Polymers are a chain of chemicals that join together to create plastics. It is how these polymers join defines how the plastic develops.
Thermoset plastic creates solid bonds between the chains that give it high structural rigidity which in turn makes the plastic very strong. They have high thermal properties and since the solid bonds create a rough texture, they have excellent adhesive properties.
The downside of thermoset plastics is that they are a one-way process. Once formed, they cannot be broken down and reused.
Thermoplastic has a completely different set of properties, they are loosely bonded, which means they have less of a structural rigidity, and are elastic and flexible. When exposed to heat, they melt. The surfaces are smoother than thermoset so have poor adhesive properties.
Thermoset uses
The automotive industry uses thermoset plastics in places where high durability and heat are commonly found. So, you will find thermoset in the engine bay, for instance.
Polyester and epoxy resins are made from thermoset because of it’s adhesion properties as well as it’s head properties.
Bakelite is used for plugs and sockets, precision made parts and vehicle brake cylinders.
Melamine and urea formaldehyde is used in household items as well as construction materials.
Thermoplastic uses
I’ve enclosed the recycling numbers that apply to these plastics along with their letter codes for recycling.
Nylon (Polyamide /PA) is used in clothing, heat resistant composite material, mechanical and automotive parts.
Polyethylene (PET 1 /HDPE 2 /LDPE 4) is used to make drums, gas tank coatings, milk bottles, squeeze bottles, jugs, movable machine parts, bullet-resistant vests, laundry detergent containers. It is also used to heat wrap material to keep out moisture.
Acrylic (Methyl methacrylate 7) is used for battery covers, lightweight glass alternative, vehicle light covers, eye lenses, as bone cement in medicine.
Polypropylene (PP 5) is used to create toys, sanitary tissues, heat-proof medical equipment, rope, string, plastic seats, laboratory equipment, detergent-proof food containers, auto mobile components, and folders.
Polycarbonate (PC 7) is used for clear sheeting where strength is required. It can be used to replace glass, and can also be used for thermal insulation by implementing multiple layers.
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC/V 3) is used to make cabinets, fume hoods, tanks, electrical insulation, toys, pipes, fittings, flooring and medical devices.
ABS (Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene /ABS) is used for monitor/TV cases, coffee makers, cell phones, calculators, most computer plastic, Lego bricks, most 3D printed parts that are not bioplastic such as PLA.
Polystyrene (PS 6) is often thought of only in it’s expanded form. It is not biodegradable, and it’s high strength makes it ideal for use under railway lines that are more prone to landslides. It can anchor together as it has a high surface area and prevents soil from moving. It can also be extruded and is available in sheet or moulded form. CD cases for example are polystyrene. Expanded PS can be dissolved in petrochemical alcohols such as acetone or melted in an oven to produce a solid mass that takes up less space than it’s expanded form.